Kia Stinger CK: Engine Control System / CVVT Oil Temperature Sensor (OTS)
Specifications
| Specification |
|
Temperature [°C (°F)] |
Resistance (kΩ) |
|
-40 |
52.15 |
|
-20 |
28.82 |
|
0 |
14.08 - 19.45 |
|
20 |
2.16 - 2.78 |
|
40 |
1.11 |
|
60 |
0.54 |
|
80 |
0.26 - 0.32 |
|
100 |
0.16 |
|
120 |
0.1 |
|
140 |
0.06 |
Description and operation
| Description |
Continuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT) system advances or retards the valve timing of the intake and exhaust valve in accordance with the ECM control signal calculated by the engine speed and load.
By controlling CVVT, the valve over-lap or under-lap occurs, which in turn improves fuel efficiency, reduces exhaust gases (NOx, HC) and improves engine performance by reducing pumping loss, generating internal EGR effect, improving combustion stability, improving volumetric efficiency and increasing expansion work.
This system consists of the CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) which supplies the engine oil to the cam phaser or runs out the engine oil from the cam phaser in accordance with the ECM PWM (Pulse With Modulation) control signal, the CVVT Oil Temperature Sensor (OTS) which measures the engine oil temperature, and the Cam Phaser which varies the cam phase by using the hydraulic force of the engine oil.
The engine oil released from the CVVT oil control valve varies the cam phase in the direction (Intake Advance/Exhaust Retard) or opposite direction (Intake Retard/Exhaust Advance) of the engine rotation by rotating the rotor connected with the camshaft inside the cam phaser.

Schematic diagrams
| Circuit Diagram |

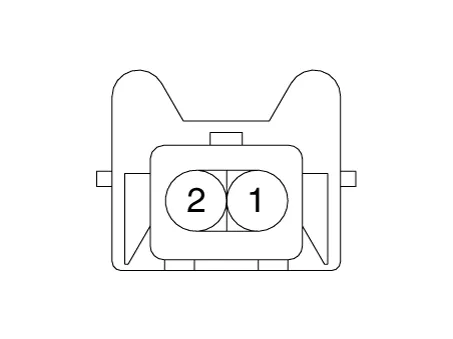
Harness Connector
Repair procedures
| Inspection |
| 1. |
Switch "OFF" the ignition. |
| 2. |
Disconnect the OTS connector. |
| 3. |
Remove the OTS. |
| 4. |
After immersing the thermistor of the sensor into engine coolant, measure resistance between the OTS terminals 1 and 2. |
| 5. |
Check that the resistance is within the specification.
|
| Removal |
| 1. |
Switch "OFF" the ignition and disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal. |
| 2. |
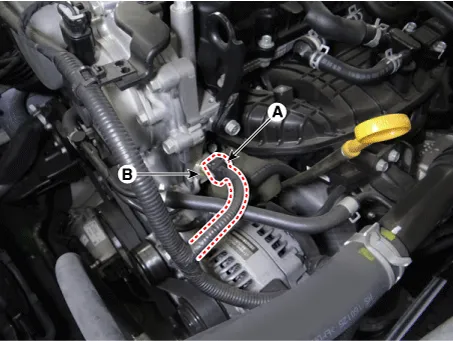
Disconnect the oil temperature sensor connector (A). |
| 3. |
Remove the oil temperature sensor (B).
|
| Installation |
| 1. |
Install in the reverse order of removal.
|
Other information:
Service data Service Data Items Inner side Outer side Front driveshaft Joint type HUJ#26 WTJ#24 Max. permissible angle 28° 54° Rear driveshaft Joint type CGJ#26 CGJ#26 Max.Special service tools Special Service Tools Tool Name / Number Illustration Description Piston expander 09581-11000 Spreading the front disc brake piston Brake bleeding procedures Adjustment Brake System Bleeding • Do not reuse the drained fluid.Categories
- Manuals Home
- Kia Stinger Owners Manual
- Kia Stinger Service Manual
- New on site
- Most important about car